Causes And Prevention Methods Of Weft Shrinkage In Looms (Fabric Surface, Fabric Edge)
The causes and prevention methods of weft shrinkage in weaving machines (fabric surface, fabric edge) are applicable to 1511, 1515 and other models of shuttle weaving machines. The reasons for weft shrinkage in weaving machines are found from the aspects of shuttle design, shuttle force, weft yarn setting, shuttle box components, etc. The prevention and control of fabric surface weft shrinkage starts from the maintenance of weft yarn setting, shuttle weft tension, and various parts related to shuttle flight.
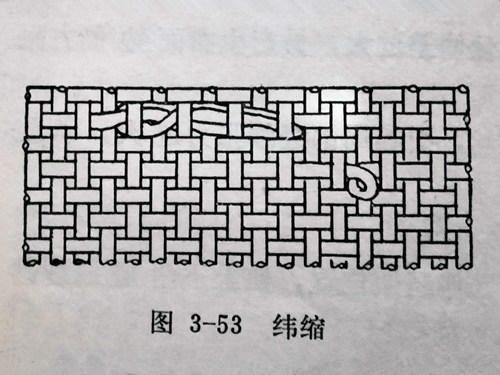
The defect of warp yarn twisting and weaving into the fabric or exposing the fabric surface in a circular shape is collectively referred to as weft shrinkage defect, as shown in Figure 3-53. To understand the process of this defect, we must first start with the weft yarn itself. The weft yarn is made by stretching and twisting cotton fibers, and after twisting the weft yarn, it gains potential reverse twisting force. During the weaving process, if the twisting force of the weft yarn exceeds the tension of the weft yarn leading into the shuttle, it may cause knots at the weak loops of the yarn and weave into the fabric or expose the fabric surface. In addition, although the reverse twisting force of the weft yarn is balanced with the tension when the weft yarn is introduced into the shuttle, during the beating process, when the reed pushes the weft yarn to move along the warp yarn and encounters larger seed breaking impurities on the warp yarn, it will also cause an imbalance in the forces between the two sides, resulting in the weft yarn appearing in a loop shape on the fabric surface or weaving into the fabric.
From the above analysis, it can be concluded that there are two causes of weft shrinkage: firstly, the yarn twist is not yet set, resulting in reverse twisting force; Another issue is that during the process of shuttle feeding and beating, there may be certain obstacles that prevent the tension of the weft yarn from being sufficient to overcome its reverse twisting force.
I. On site analysis and specific reasons
(1) If there are shrinkage defects on a large area of machines in the workshop, they are mostly caused by the following factors:
1. The weft yarn has excessive twist or insufficient twist setting treatment. This type of weft yarn has a strong potential for reverse twisting and twisting force,Exceeding the tension when weaving the weft yarn can cause the weft yarn to twist and produce weft shrinkage defects.
2. If the weft yarn is too dry or the relative humidity in the workshop is too low, it is easy to produce weft shrinkage defects. This is because the potential twisting force of the weft yarn is closely related to the moisture content of the weft yarn. Generally, weft yarns with high moisture regain are less prone to weft shrinkage defects; On the contrary, when the weft yarn is dry, it is more prone to weft shrinkage defects.
(2) The weft shrinkage defect on the fabric surface mostly occurs on the half of the fabric surface on the shuttle changing side, and often occurs during the large yarn period. The cause is:
When the shuttle flies out of the shuttle box on the shuttle changing side, the tension of the weft insertion is small, and due to the long length of the weft yarn left outside the shuttle, the weft yarn is relatively loose when it is guided into the shuttle mouth, which is prone to weft shrinkage.
When the weft yarn in the shuttle is in a large yarn, the angle between the line segment from the exit point of the weft tube to the entrance of the yarn guide porcelain eye and the centerline of the weft tube is large, and the distance between the two points and the line segment is also short. Therefore, the frictional resistance between the weft yarn and the surface of the weft tube is small, making it easy to produce weft shrinkage defects.
(3) The reason for the regular occurrence of twisted and contracted meridians is:
1. When the throwing force is high or the buffering force is low, there is a lot of loose weft yarn during the process of the shuttle entering the shuttle box, and the shuttle is prone to bounce back, causing the weft yarn between the shuttle and the shuttle box to be squeezed and twisted widely; When the shuttle flies again, if the knot cannot be untied, it will weave into the fabric and form a warp. Due to the similar process conditions of throwing the shuttle one after another, the location where the warp occurs is also relatively close.
2. The components of the shuttle box are fuzzy, making a section of weft yarn left outside the shuttle after entering the shuttle box easy to be pulled and twisted. When the shuttle flies again, if the knot cannot be untied and woven into the fabric, it will become weft shrinkage.
(4) The causes of fabric dispersion and weft shrinkage:
1. The shuttle's guiding tension is too small to resist the potential reverse twisting force of the weft yarn, which can easily lead to weft shrinkage.
2. The shuttle movement is unstable, especially when it collides left and right when entering the shuttle box, providing opportunities for twisting the weft yarn, which can easily lead to weft shrinkage defects.
3. The loose winding of the weft yarn increases the amount of weft yarn pulled out, and in severe cases, it may result in yarn detachment or breakage, while in mild cases, it may cause twisting and produce weft yarn defects.

(5) The causes of small circular weft shrinkage on fabric:
1. Poor hanging or stiff and rough warp yarn: After the weft yarn is introduced into the shuttle mouth, its length is usually fixed when it is flat. With the push of the steel reed, the weft yarn is pushed from the back of the machine to the front, from the inclined position to the flat position to the weaving mouth position. The tension of the weft yarn gradually decreases from high to low. In addition, during this period, the upper and lower warp yarns undergo alternating displacement movements, such as improper position of the warp frame, jumping of the warp frame, stiff and rough warp yarn, or cotton balls, which will interfere with the smooth sliding of the weft yarn, causing the tension of the weft yarn to restrain the twisting force of the weft yarn, resulting in the formation of weft shrinkage defects due to twisting.
In this case, under conditions where there is a large difference in the number of warp yarns between coarse and fine warp yarns or between the upper and lower layers (such as 4/1 satin fabrics, etc.), it is more likely to cause warp yarn tangles, resulting in more weft shrinkage defects in these fabrics.

II. Prevention and control methods for weft shrinkage defects
The prevention and control of latitude shrinkage mainly focus on the following four aspects:
(1) Weft yarn shaping
1. Natural setting of weft yarn. The weft yarn to be used for weaving shall be stored for a certain period of time, generally 24 hours. At least one shift is required to allow the weft yarn to absorb moisture naturally, so as to stabilize the weft yarn winding structure and twist. Some of the storage locations are equipped with special rooms and spray equipment, and some are directly stored in the cloth machine workshop, according to local conditions. When using natural setting method, it is necessary to pay attention to the need for a certain turnover of weft yarn and strictly implement the fixed supply system of spinning first, using first.
2. Wet and shape the weft yarn. It is an effective method to stabilize the twist and prevent twisting. Because after wetting the weft yarn, the elasticity of the fibers weakens, the plasticity increases, and due to the expansion of the volume of the fibers after moisture absorption, the mutual friction increases and the activity becomes stagnant. These conditions all play a role in stabilizing the shape of the weft yarn. Therefore, the wet treated weft yarn can remove weft shrinkage. However, excessive humidification should not be used because when the humidity of the weft yarn is too high, the adhesion force between the yarn layers increases, the air ring of the weft yarn shrinks, and the friction between the weft yarn and the end of the weft tube increases, which can easily cause weft breakage.
So the humidification of weft yarn should be properly controlled according to the specific situation. As for the forms of humidification, there are generally the following:
1. Heating and humidification in the steam room has the advantage of good weft yarn shaping effect, but the disadvantage is that it is easy to damage the weft tube.
2. Water immersion and wetting: The advantage is that the equipment is simple, but the disadvantage is that the labor intensity is high during manual operation, the wetting is uneven, and the water stored in the weft tube is prone to contaminate the weft yarn.
3. Humidification of the dehumidifier: The advantage is that it provides uniform moisture, but the disadvantage is that sometimes the weft tube is prone to rolling damage and dirty yarn.
The soaking method and humidification of the humidifier should be based on the yarn count and winding density, the severity of weft shrinkage, and other factors. An appropriate soaking agent should be added to the water and the storage time after humidification should be reasonably determined to thoroughly remove weft shrinkage defects.
(2) Appropriately increase the warp tension of the shuttle
A guide device should be installed inside the shuttle that does not increase the breaking and releasing tension, such as 1-4 steel wires, 1-4 loops of shuttle hair, 1-4 nylon rings, fur, velvet, rubber bands, airplane spring leaves, etc. But these measures must be selected according to the specifications of the fabric variety.
(3) Carry out maintenance work on various components related to shuttle flight
1. Check and repair the shuttle and buffer device to ensure their proper functioning and prevent the shuttle from bouncing back.
2. Do a good job in shuttle maintenance, keep the shuttle surface smooth, and ensure that the weft tension device is complete and functioning properly.
3. Strengthen the maintenance work of the shuttle track, ensure the smoothness and correct position of the shuttle box components, and ensure stable shuttle flight.
4. Check and repair the various components of the opening movement, that is, correct the position of the warp frame, adjust the tension of the hanging warp frame, prevent the warp frame from jumping, so that the weft yarn can smoothly slide along the warp yarn and enter the weaving mouth during beating.
5. Improve the quality of sizing and ensure proper temperature and humidity management in the workshop.
Taken from "1511 Loom Malfunction and Repair"








